Electromagnetic fields in the workplace
Finding out which sources are present in our workplaces is essential if we want to take control of our own electromagnetic environment.
Electromagnetic fields in the workplace
Employers are now required to implement a risk management policy that fully integrates electromagnetic fields into their control plans. This approach applies to all types of environment, whether tertiary, industrial or hospital.
Depending on the nature of the company's activity, there may be three types of electromagnetic field in the workplace. Static fields can be added to the more common high and low frequency fields. While high frequencies generally predominate in tertiary environments, industrial environments can expose employees to all three types of electromagnetic field. Depending on the activity, there is a real risk of exceeding exposure limits, and employers must take this into account in their risk prevention policy.

Although already present for a long time in some industrial applications, high frequencies have above all penetrated our working environment with the advent of radio communications.
Also known as radio frequencies, they are used for their ability to propagate in our atmosphere and are therefore very practical for wireless communications systems.
Today, the mobile phone, which has almost replaced the wired telephone in our offices, and the consumption of data via the Internet, are major contributors to the evolution of our electromagnetic working environment.

Indoor mobile telephony
Need to carry out specific assessments for workers with no particular risks, workers with particular risks and workers with active implants.

Wi-Fi terminals
Need to carry out specific assessments for workers with active implants.

Cordless telephones (DECT)
Specific assessments are required for workers with active implants.
Low-frequency electromagnetic fields are used for their ability to carry electrical energy. It is therefore normal to find them predominantly in industrial environments.
All devices that consume a lot of electricity (welding sets, electrical cabinets, etc.) are therefore likely to radiate very strong fields and have an impact on our direct working environment.
Fortunately, at these frequencies, the field propagates very poorly and attenuates very strongly with distance. It is therefore useful to study each workstation carefully to determine its exposure.

Work on wind turbines
Need to carry out specific assessments for workers at particular risk and workers with active implants.
Welding workstations
Need to carry out specific assessments for all categories of workers.
Induction heating
Specific assessments are required for workers with no particular risk, workers with particular risk and workers with active implants.
Static fields are generated by magnetic materials (which are used to make magnets) that are naturally present in our environment.
In fact, our planet is a large magnet that constantly generates a static magnetic field. It is this field that our compass uses to find North.
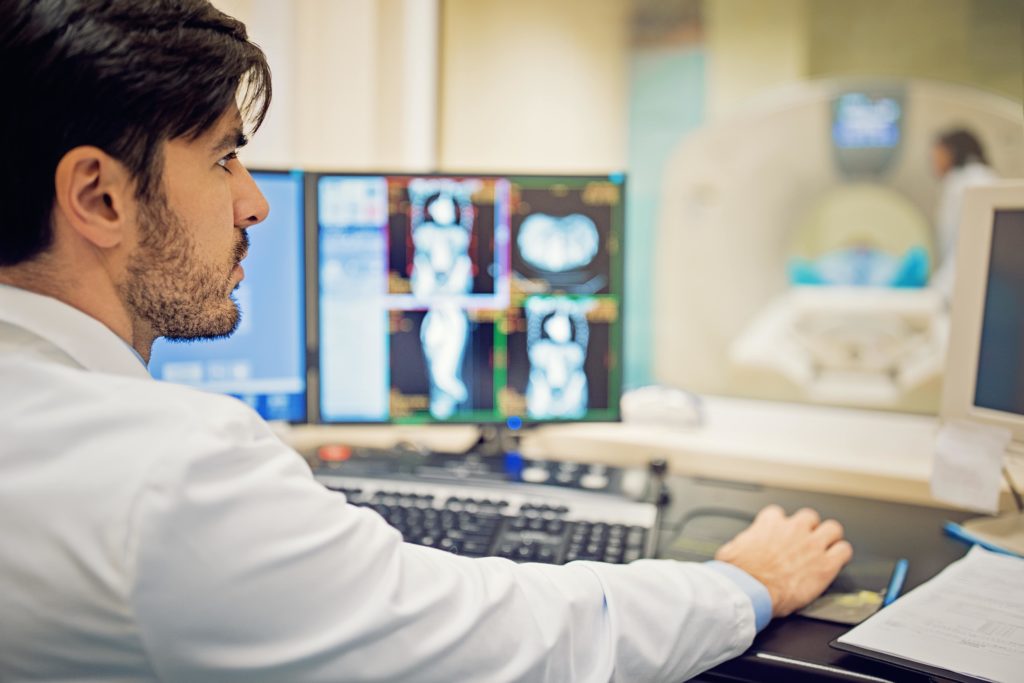
Some manufacturers use it for very specific applications, producing huge magnets for use in wind turbines, for example. In the medical sector, MRI scanners are also fitted with magnets.
This represents a considerable risk, given that magnets of this type can project very large metal parts by attraction. It is therefore vital to identify these areas in the working environment.
Electrical converter
Specific assessments are required for workers with no particular risks, workers with particular risks and workers with active implants.
MRI
Need to carry out specific assessments for workers with no particular risks, workers with particular risks and workers with active implants.
To stay informed about electromagnetic fields in the workplace, enter your email address below
"*" indicates required fields
AT WORK
Latest news
EMF & HEALTH AT WORK
Am I exposed to electromagnetic fields in the workplace?
To assess your level of exposure to electromagnetic fields at work, we recommend that you contact your employer and those responsible for health and safety at work (HSE/QHSE). The aim is to obtain specific information on the regulations applicable to your sector, identify any sources of emissions and discuss any concerns you may have. Do not hesitate to check whether your employer informs you of the measures taken to assess and reduce your exposure.
It is important to note that since 1 January 2017, employers have been required to assess the risks to their employees and ensure compliance with the limit levels set by the regulations. Equipment likely to generate electromagnetic fields must be identified, and measures must be taken if there is a risk of regulatory levels being exceeded.
To find out more about compliance solutions for your company and to receive support…
Am I affected by the risks associated with electromagnetic fields in the workplace?
Although all workers are concerned, certain groups are considered to be exposed to a particular risk from electromagnetic fields. This is the case for pregnant workers, for example. It is therefore necessary for their employers to examine their exposure separately from that of other workers considered to pose no particular risk.
01
Wearers of active implanted medical devices
(AIMD): cardiac pacemakers and defibrillators, cochlear implants,
brain stem implants, inner ear prostheses, neurostimulators, retinal encoders, implanted perfusion pumps, etc.
02
Wearers of passive implanted medical devices
containing metal: artificial joints, pins, plates, screws,
surgical staples, aneurysm clips, stents, heart valve prostheses, annuloplasty rings, metal contraceptive implants and AIMD casings.
03
Workers wearing medical devices
on the body: external hormone infusion pumps, for example.
ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS
What does the law say?
In France, the regulations governing workers’ exposure to electromagnetic fields are mainly set out in European Directive 2013/35/EU and implementing decree no. 2016-1074.
It stipulates that the employer is required to assess the risks associated with electromagnetic fields present in the workplace and to take the necessary measures to ensure the protection of workers’ health and safety.
Depending on the sector of activity, this includes identifying sources, measuring exposure, using appropriate personal protective equipment, setting up controlled work areas and training workers in the risks and preventive measures.






